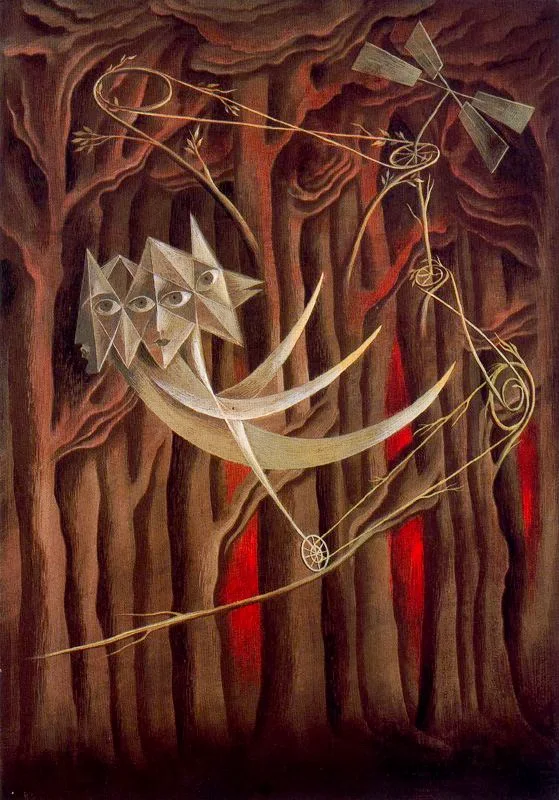
Caravan
Αινιγματική και ασφυκτικά κλειστοφοβική και ταυτόχρονα ανάλαφρη και διάφανη η Remedios Varο... Γεννήθηκε το 1908 στη Καταλωνία και πέθανε το 1963 στο Μεξικό.
Ladies' Suit, 1957
In 1908, Remedios Varo was born into a complicated family setting in the small town of Gerona, Spain. Her mother was a deeply religious woman, committed to Catholic spirituality, while her father was an atheist engineer, whose life was built on reason, mathematics, and free thinking. These two forces, the mystical and scientific, greatly influenced Remedios's work throughout her artistic career. When she was nine, the Varo family moved to Madrid, where Remedios was formally educated at a religious school; however, at night she stealthily read science books and taught herself to use her father's engineering tools. At age sixteen, Remedios escaped the world of the convent to attend the Academia de San Fernando in Madrid, where she was a classmate of Salvador Dali until he was expelled for recalcitrance.
Farewell, 1958
"In clear contrast with the surrealist tendencies seeking 'liberation' from the underground depths of unconscious desire, the art of Remedios Varo projects itself toward the opposite extreme: toward the supra-conscious understanding of a 'superior' reality... Remedios consciously "constructs" an idealized world in which harmony and sublimity reign." Juliana Gonzales, art historian.
The World Beyond
At age twenty-two, Remedios's artistic career began to take off. She participated in her first group exhibition, married fellow artist Gerardo Lizarraga (with whom she stayed married for only two years), and moved to Barcelona with him. With the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War in 1936, Varo decided to move to Paris with the poet Benjamin Peret, who was a close companion of the so-called father of Surrealism, Andre Breton. With Peret by her side, Remedios was brought into Breton's circle of Surrealist artists, yet she often felt overshadowed by Peret's presence and notoriety. Because of her gender, she was never considered an integral member of the Surrealist group; on the fringe, she participated in Surrealist shows only occasionally. It was partly due to her marginalization and partly due to her inability to relinquish complete control over her artistic creations, that many art historians, and even Remedios herself, did not consider her to be a strict Surrealist.
Varo's artistic
style--part surrealistic, part realistic--truly blossomed when she fled
Nazi-occupied France and moved to Mexico in 1941. About her move to Mexico,
Varo remarked "I came to Mexico searching for the peace that I had not
found, neither in Spain because of the revolution nor in Europe because of the
terrible war. For me it was impossible to paint amidst such anguish."
Although she initially felt like an exile, Remedios found home in Mexico, and
she realized that she ultimately experienced more artistic and intellectual
freedom there than she had anywhere in Europe. "I can see that my
life" she said, "not only in material or emotional terms, but also my
intellectual life, is here in [this] land I sincerely love with all its faults,
shortcomings, and hardships." It was her deep love for Mexico that kept
her from returning to Paris with Peret in 1947, and instead pushed her to
explore another Latin-American country, Venezuela, where her mother and brother
Rodrigo then lived. Rodrigo was chief of epidemiology for the Ministry of
Public Health in Venezuela, and under his tutelage, Remedios began studying and
drawing mosquitoes for a campaign against malaria. Again, her artistic work
dipped into the scientific realm.
Exploring River of The Source Orinonoco
In the early 1950's Remedios returned to Mexico and married Walter Gruen, an Austrian political refugee, and at this time she pledged to devote her life entirely to painting. It was then that her style fully matured to include its unique brand of symbolism and iconography: women with heart-shaped faces that mimic her own, and slit-like eyes that convey a sense of loneliness and a lack of fulfillment. This loneliness is highlighted again and again as Varo paints her characters trapped in one environment or another, whether it be a tower in the sky, like in Celestial Pablum, a room without a door, or even a chair that seems to have a magical power that forces its victims to stay put, like in Mimetismo, which is currently in the Museo de Arte Moderno in Mexico City. In all of her works, one senses the artist's own isolation; yet this seclusion is coupled with internal revelation and astonishment that takes the form of a mysterious ray of light or patches of luminosity on the canvas. This combination of isolation and revelation is mirrored in Remedios's overall juxtaposition of whimsy and precision, a blend that many art historians find unsettling. Varo uses her scientific knowledge to paint scenes that place scientifically accurate machinery in an unrealistic fantasy world. Essay by Lauren A Kaplan.
Fantastic animal, 1959
Allegory of Winter, 1948
Rheumatic pain
Plant, 1960
Unexpected view
Aurora, 1962
Homo rodans, 1959
Floral bouquet with birds, 1960
Gypsy and harlequin, 1947
Premonition, 1953
Harmony, 1956
This portrait of Doña María was painted by Remedios
just two years after she entered the Academia de San Fernando. Salvador Dalí, the Surrealist painter, was
also a student of the Academia in Madrid, around the time frame Varo
attended. (Kaplan 29)
Plant architecture, 1962
Vagabond
Witch going to the
Sabbath, 1957
Lady Godiva, 1959
The World, 1958
Christmas turkey
Malaria, 1947
Garden of love, 1951
Cats Paradise, 1955
As the Volante, 1962
The battle
The task
By Aquarium, 1961
The Pollution of the Water
Creation with astral rays, 1955
The rich, 1958
Pain, 1948
Trasitoen Espiral
Creation of the Birds
The Message, 1935
Lunar reflection
The emigrants
Still life Reslicitando, 1963
Eyes on the table, 1938
Tightrope walkers, 1944
The Juggler
Visit to the plastic surgeon, 1960
Cold, 1948
The Labrador, 1958
Rheumatic pain, 1948
Towards The Tower
"In
Surrealism, the artist attempts to depict a time/space that is somewhere in
between reality and dreaming. Varo
accomplished this goal, but was dissatisfied with the traditional role of women
in Surrealist painting: female as the muse or object. In her work, she shifted the role of woman to
embody the heroine, explorer, and creator." (Congdon, 291)
O Octavio Paz της αφιέρωσε το ποίημα του "Remedios Varo’s
Appearances and Disappearances"
With the visible violence of wind scattering
clouds, but with greater delicacy, as if she
painted with her eyes rather than with her
hands, Remedios sweeps the canvas clean and
heaps up clarities on its transparent surface.
In their struggle with reality, some painters
violate it or cover it with signs, explode it
or bury it, flay it. Remedios volatizes it:
it is not blood but light that flows through
its body.
She slowly paints lightening-quick apparitions.
Appearances are the shadows of archetypes.
Remedios does not invent: she remembers.
Except that these appearances resemble nothing
and no one.
Sea voyages within a precious stone.
A speculative painting, a mirror-image painting:
not the world in reverse, but the reverse
of the world.
The art of leviatation: the loss of gravity,
the loss of seriousness. Remedios laughs,
but her laughter echoes in another world.
Space is not an expanse but a magnet attracting
Appearances. A woman’s hair… the strings
of a harp… the sun’s rays streaming down
… the strings of a guitar. The world seen
as music: listen to Remedios’s lines.
The secret theme of her work: harmony… lost
equality.
In Appearance she paints Disappearance.
Roots, fronds, rays, locks of hair, flowing
beards, spirals of sound: threads of death,
of life, of time. The weft is woven and un-
woven: the unreality that we call life, the
unreality that we call death… only the canvas
is real. Remedios the anti-Moira.
She does not paint time, but the moments when
time is resting.
In her world of stopped clocks, we hear the
flow of substances, the circulation of shadow
and light: time ripening.
Forms seek their own form, form seeks its own
dissolution.
- Octavio Paz